Different Types of Gloves & When to Use Them | Advantages & Disadvantages

Gloves are an indispensable part of your personal protective equipment which saves your hand from the hazardous working environment, stops spreading germs, contaminants in the environment or objects you are handling from your hands.
Whether you work in construction sites or go skiing in the freezing temperature of the winter months, you always accompany the glove. Keeping in mind the potential threats you may get in your working site, gloves are made accordingly to save your hands.
Such as, if your work involves cutting with an industrial chain or rotary saw etc, you need cut-proof, puncture-proof gloves. If you work in the food industry, you should wear FDA approved food preparation gloves.
The protective capabilities of a glove depend on the materials they are made of and their strategic construction methods.
In this article, we will discuss the various materials used in the making of gloves, and the properties of those materials.
This guide will help you to find the perfect gloves for your needs.
What are glove materials?
Glove materials can be made of numerous products that are natural or synthetic. Based on the properties and characteristics of the glove material, the workability is determined.
The different types of glove materials and their properties
Here is the list of a few most commonly used glove materials and their properties and usability area.
#1 Nitrile Gloves
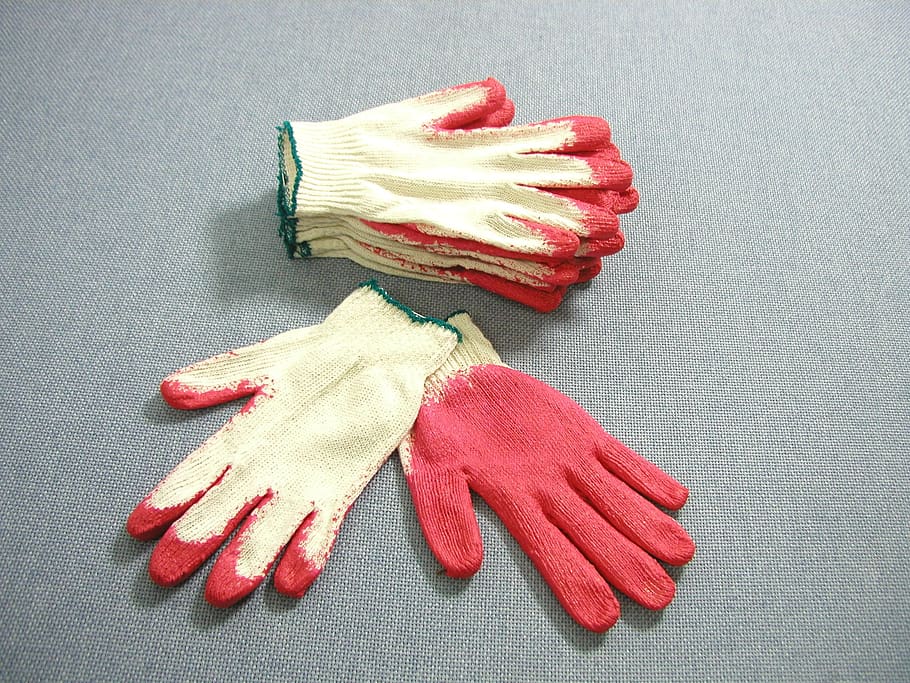

Nitrile rubber is a type of synthetic rubber used as a replacement for natural rubber because of its certain useful properties. This is a copolymer of Butadiene and Acrylonitrile. This is also known as Buna-N, NBR and trade names like Nypol, Europrene-N etc.
Advantages of Nitrile rubber:
Nitrile rubber has greater resistance to mineral oils, vegetable oils, greases, and low permeability to gas than natural rubber. It also possesses great elasticity, tensile strength and puncture resistance.
These properties depend on the amount of ACN present in the rubber. On average NBR contains 15-50% of acrylonitrile. More the amount, better the resistance against oil, gas and abrasions but less the glass temperature i.e becomes less flexible in lower temperature.
It also offers some protection against viruses and mild heat, dilute acid and alkalis.
Disadvantages:
Poor resistance against ozone, weathering.
Very limited resistance against heat and becomes rigid in low temperatures. ( stable between -40C to 108 C ).
When to use:
Because of these properties, nitrile coated gloves can be used if you work in the oil and gas industry or need to protect the hand from being wet or in other industries as an alternative to latex gloves if you have a latex allergy.
#2 Polyurethane Gloves
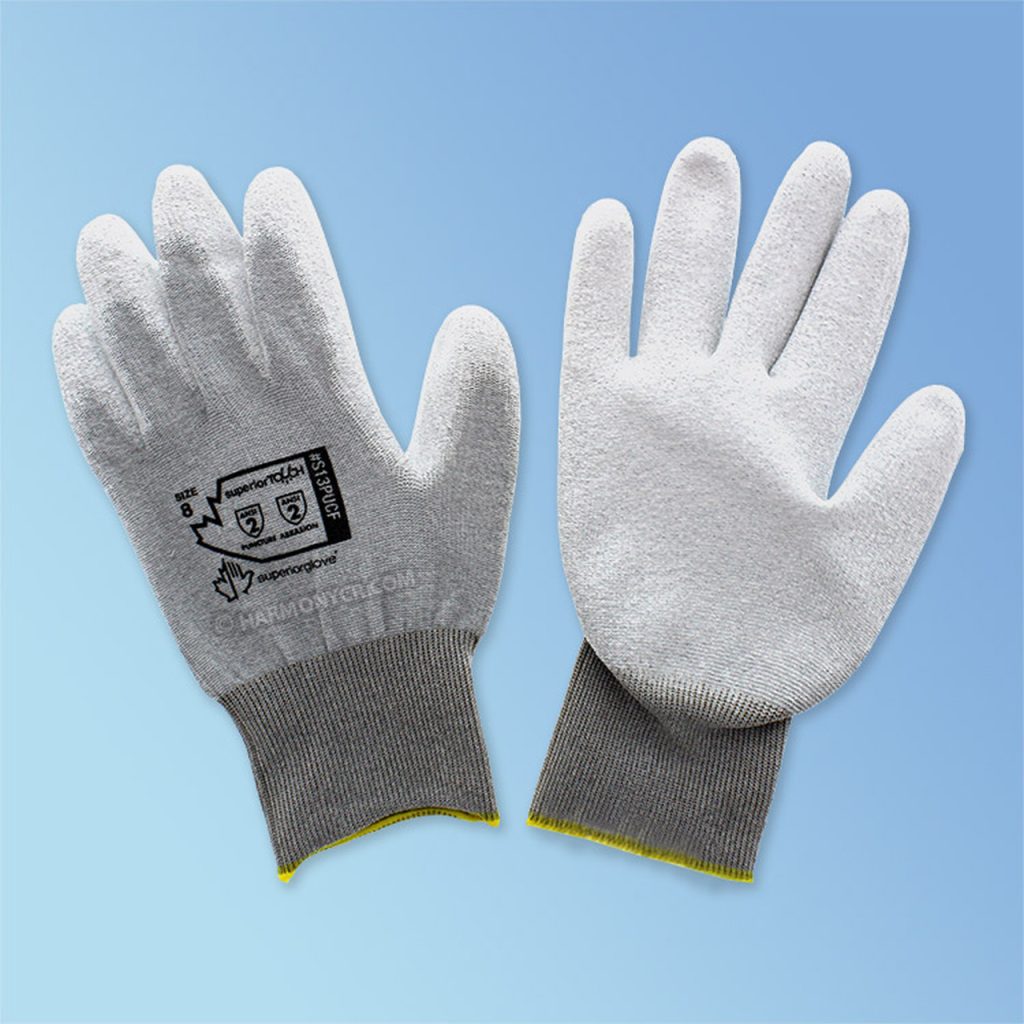

PU or polyurethane is probably the most underrated coating material in the gloves industry. This is a class of polymer having versatile applications because of its distinctive manipulable properties.
It is made using an organic ( aliphatic or aromatic ) diisocyanate and a diol. The PU foam is prepared by adding water to the reaction process. Water ( H2O ) reacts with the isocyanate group to produce urea and carbon dioxide which acts as a blowing agent within the material.
Properties of the PU depends on the aromatic or aliphatic group present in the backbone. Thus, we can create a PU rubber having certain characteristics to solve a particular problem.
In gloves manufacturing it is used because of these properties mentioned below.
Advantages of PU:
High resistance to water, oil, hydrocarbons, grease, oxygen, ozone.
It has high tensile strength, flexibility and resiliency range.
It is abrasion-resistant and tolerates harsh environments such as high temperatures, exposure to chemicals rarely cause any degradation to the materials.
It is high cut and tear-resistant, and the manufacturing is economical.
Disadvantages of PU:
Every good thing comes with a price. Despite being such a versatile material, PU also has some cons worth mentioning.
- PU release odor and toxic fumes if burnt. Regular exposure with it can cause a serious health issue.
- Most of the PU coated gloves are ANSI abrasion level 1 type, so, less durable.
- It makes your hand sweaty, it is not breathable.
#3 Cowhide leather Gloves
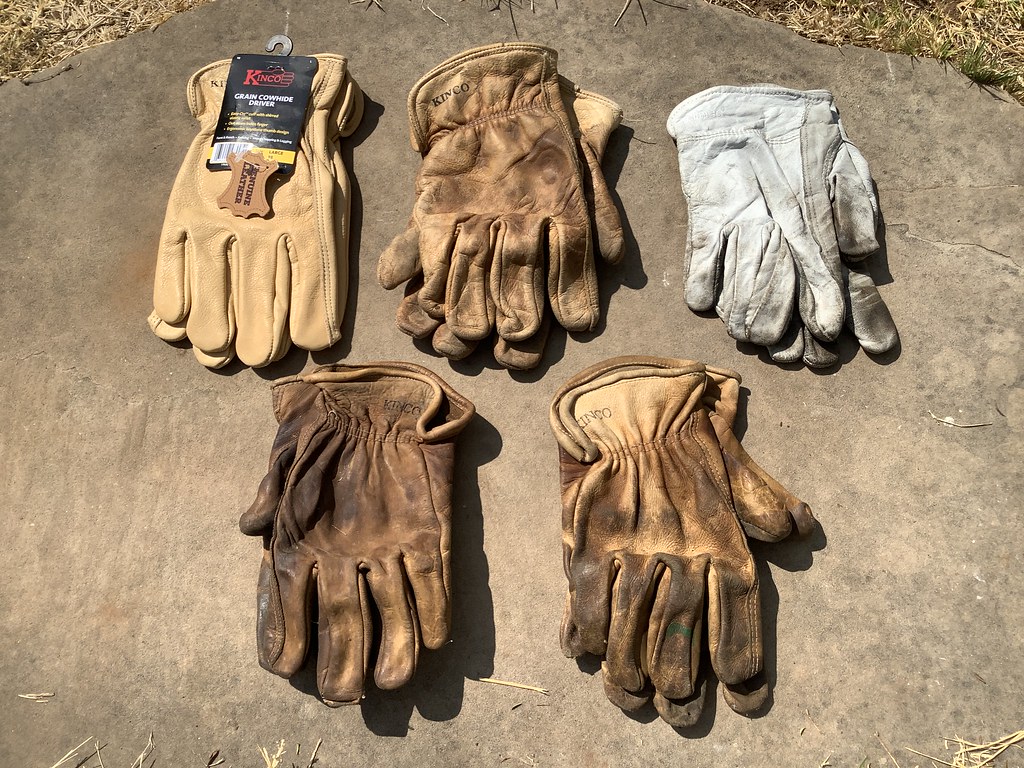

Known for strength and durability, cowhide leather is the most common choice for gloves. A very good insulator, Cowhide leather tends to mould itself according to the shape of the wearer’s hand. With the ability to withstand moisture for a very long tenure, the cowhide leather is quite comfortable for long-duration wear.
However, it must be remembered that if cowhide leather is split, then the inner split leather is not as moisture resistant as the whole grained cowhide.
Advantage:
- A very good insulator, so it is suitable for use in low-temperature scenarios
- It is very strong and does not wear out easily
- Durability aside, they have a very good abrasion resistance
- Is very well resistant to heat and suitable for work under high temperature.
Disadvantage:
- Compared to the various other types of leather, cowhide is heavier.
- The softness index of cowhide leather is also not very good as they have a very grainy and rough surface.
- The gloves tend to become brittle on continued use.
Where to use them:
- Commonly used at the construction site for heavy lifting. It provides a sturdy grip and protects the hand from common cuts and bruises while working with gravel and stone chips.
- A preferred choice for working in ice storage facilities and colder conditions as the gloves are insulated and resistant to moisture and are slip-proof.
- Bee workers used cowhide gloves to prevent bee stings from penetrating the skin.
In this helpful article, we have shared important tips and tricks on how to wash work gloves made with leather & other materials.
#4 Pigskin leather Gloves
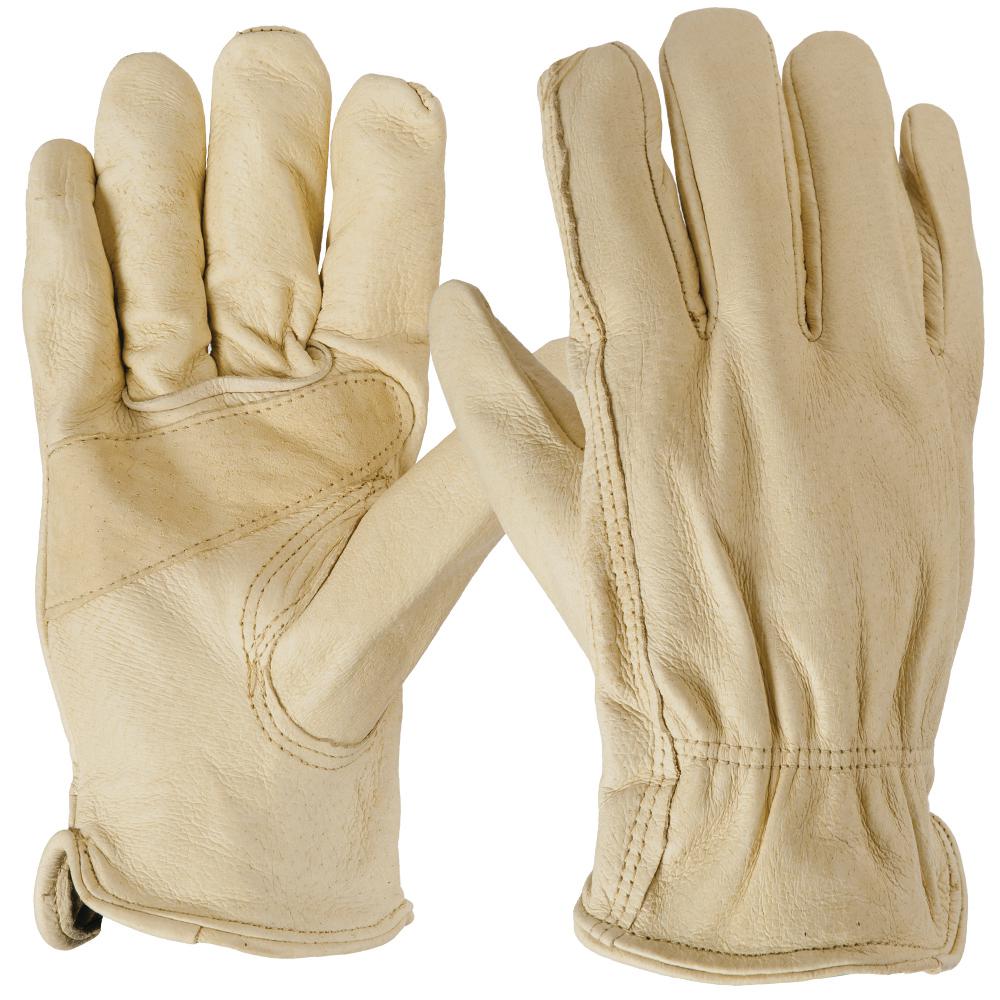

Pigskin gloves are comparatively tougher and more pliable than most other natural leathers. Resistant to moisture, the pigskin leather does not harden easily on prolonged use. An interesting trait of pig leather is that they provide very good aeration due to the microscopic hair bristle pores. This makes them very comfortable to use, especially in hotter weather conditions, a speciality when the humidity is high.
Laundering pigskin leather is far easier than Goatskin or cowhide as it does not easily lose its shape and functional aspects.
See more properties of pigskin leather.
Advantage:
- Very flexible and dextrous in nature, thus allowing better mobility of the fingers
- Repellent towards both Oil and Water
- Has a very good stain repellent property
- Requires minimal maintenance
- Very affordable
Disadvantage:
- Does not do well in colder temperature as it lacks basic insulation
- Does not have a wider feature range for usability
- Pigskin is water repellent. However prolonged contact with moisture can cause absorption of fluid through the surface bristle pores.
Where to use them:
- Suitable working gloves for the hot and humid sector as it facilitates better aeration and prevents sweating of hands
- Usable for yard work and gardening
#5 Goatskin leather gloves

Compared to cowhide and pigskin, goatskin leather is far more dextrous. In addition to it, the tensile strength index is very high, thus making them stiffer in comparison to the other two. Well resistant to abrasions and tears, Goatskin is very supple and soft to touch. Though they feel very delicate, Goatskin is tough and water-resistant due to the presence of lanolin.
Advantage:
- Offers very good insulation, though it’s not as par cowhide.
- High adaptability index as the gloves keeps the hands warm in winter and cooler in summer.
- Has a very rugged and tough feel to it despite the soft and supple appearance
- Even though it is heavy, it is far lighter than cowhide
Disadvantage:
- Though it is water-resistant, however, a small amount is bound to seep in as Goatskin is not completely waterproof
Where to use them:
- Goatskin leather is best to use in the manufacturing sector, where rough handling of products is very common. Being highly resistant to abrasion and having a higher dextrous character, it seldom wears out easily.
#6 Synthetic leather gloves

An alternative to natural animal hide, Synthetic leather is more cost-effective and available. Often mistaken as real leather, they are far more durable. Being washable, they last longer without wearing out.
Another interesting feature of faux leather or synthetic leather is that they are extremely resistant to abrasion and Puncture, thus increasing their workability quotient further. Synthetic leather is a completely non-breathable fabric, so sweating is quite common in case of prolonged wear.
Advantage:
- Extremely flexible and dextrous, thus making finger movements far less strenuous and more agile.
- Being highly water-resistant, the permeability is very minimal to absolutely none.
- Offers very good resistance against slipping, thus improving the grip index.
- Resistant to chemical and oil spill
Disadvantage:
- The chemicals used to make synthetic leather can cause a toxic reaction on the skin on prolonged usage.
- The material is not environment friendly
- Synthetic leather is either partially or non-bio-degradable.
- Non-breathable
Where to use them:
- These gloves are best for use where there is a prolonged need to handle chemicals, oils, and reagents.
#7 Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) gloves

Also known as Thermoplastic elastomer gloves, the glove material of thermoplastic rubber often has similar elasticity to natural rubber. Made using copolymers of synthetic rubber, they are more expensive than other synthetic resin gloves. With a very high heat resistant coefficient, they are perfect for use in work that involves high temperatures. These non-sterile gloves are safe on the skin and come in multiple size options, thus increasing the usability index.
Advantage:
- Less expensive than vinyl gloves
- Highly durable and resilient
- Durable and dextrous, thus allowing rough handling and vigorous finger movements
- Environment-friendly alternative to latex and powder-free
Disadvantage:
- Usability is restricted to Food and beverage industry
Where to use them:
- As they are toxin-free and safe to use, they are a common choice for the food processing industry and the foodservice industry.
#8 Styrene-butadiene rubber ( SBR ) gloves

Produced by combining 75 % Styrene monomer with 25 % Butadiene, this synthetic rubber has similar look and character traits to natural rubber. Nitrile Butadiene is more commonly used in making gloves than Styrene Butadiene. It is used to make tires, rubber goods, etc.
Based on the method used in making the SBR, it shows different characteristics. The two variants are
Emulsion SBR – This functions well in lower temperatures but has low tensile strength and tear strength. So it is common to see shrinkage and tear.
Solution SBR – Has a better flexibility index and stronger tensile strength. However, it is way more expensive than the other variant.
Advantage:
- High abrasion resistance to extensive use and wear and tear
- Can withstand high-intensity impact without breaking down
- Increased resilience quotient with a very high tensile strength that is better than natural rubber
- It is completely resistant to UV exposure
- Do not degrade easily
- It is affordable and readily available.
- When combined with silica, it has better thermal conductivity.
Disadvantage:
- Lower heat resistance
- May show stiffening when exposed to a lower or colder temperature.
- Does not react well with hydrocarbons and chlorinated solvents
Where to use them:
- SBR material is used as inner padding on Synthetic and spandex work gloves to reduce vibration intensity that occurs while handling heavy duty machinery and instruments.
- Suitable for use as biker gloves due its ability to absorb vibrations as mentioned above.
#9 Cotton gloves

Cotton is a naturally breathable fibre. Hence it is mostly used to make liners for gloves to improve the aeration within the gloves. Materials like PU, Nitrile and other synthetic compounds are often used as a coating on cotton gloves to improve their inherent characteristic properties. Adding coating improves resistance to abrasion, thermal changes, punctures and also improves the grip.
Advantage:
- It is a very good baseliner for any gloves.
- They are very comfortable to use in hot and humid conditions as they absorb moisture.
- It is environmentally friendly and biodegradable.
- When added as an external layer on rubber or other glove material, it improves surface grip tension and adds an extra layer of protection.
Disadvantage:
- Offers minimal protection against chemicals, abrasion, Puncture, and thermal changes.
- Soaks water and thus conducts static.
- Can leave behind fingerprints when moist.
Where to use them:
- While handling delicate paintings and artwork, cotton gloves are mostly used as they are very delicate and soft on the finer aspects of these precious commodities.
- As accessorization with clothing
- The handling steering wheel of cars
- Food processing industry
#10 Woolen gloves

Made from natural sheep and other animal hair, wool is one of the most eco-friendly glove fabrics. Extremely good thermal insulation aside, wool does not distort easily, thus making them a very long-lasting fabric of choice for gloves.
Advantage:
- They are naturally resistant to UV-rays
- Very lightweight and shrink resistant
- Wool does not stain easily
- Cost-effective and durable
- It is resistant to microbes and bacteria, thus reducing the chances of skin infections.
Disadvantage:
- Porous, so is not safe for use in handling oils and chemicals
- Is neither waterproof nor water-resistant.
- Delicate, thus with very minimal abrasion resistance
Where to use them:
- Woolen gloves are excellent thermal insulators, thus making them perfect for use against frostbites during extremely cold winters. They can also be paired as liners with other water-resistant gloves.
#11 Polyester gloves
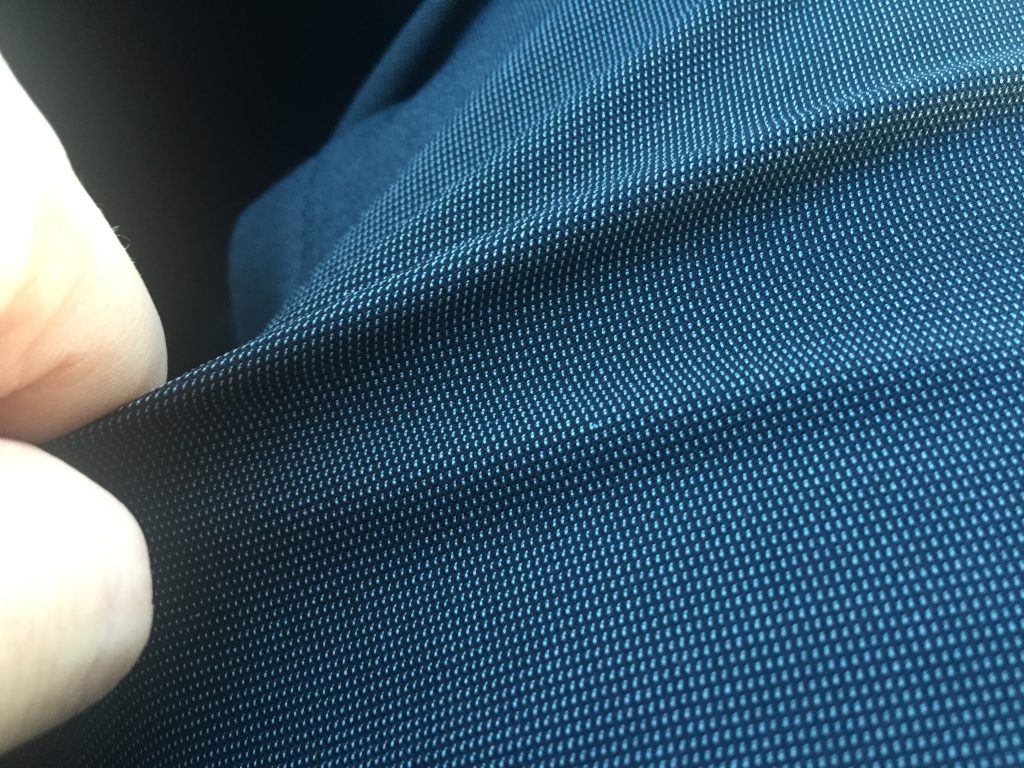

Similar to cotton glove material, Polyester is highly flexible and elastic. They rarely shrink and are one of the most durable fabrics of choice. However, Polyester is not as breathable as cotton, thus reducing its comfortability to a great extent. Cotton blended polyester fibre, better known as Polycotton, is one of the common glove materials used.
Advantage:
- Has an optimal heat resistance ability
- It is very durable and can withstand stretch and strain remarkably well without tearing
- Does not puncture easily
- Does not loses its dimensional stability despite multiple washing
- Does not fade or lose color easily
Disadvantage:
- Does not offer sufficient friction and is more prone to slipping.
- It is not suitable for prolonged use under high temperatures as it is not a breathable fabric, thus causing excessive sweating.
- Relatively cheaper
Where to use them:
- Generally is used in oven mitts and gloves.
- Suitable for use in handling and assembling of goods. Sometimes, mixed with other fabrics such as nylon, spandex etc.
#12 Chloronite gloves

One of the best creations of the 21st century, Chloronite is a nitrile-free compound that is resistant to even the harshest of chemicals and radioactive materials. Extremely lightweight and flexible, Chloronite gloves have become necessary while handling hazardous solvents, fuels, chemicals, and other hazardous products. The textured finger allows better grip, while the material stretchability allows ease of movement.
Advantage:
- It is reusable and does not disintegrate easily
- Resistant to all forms of chemicals and solvents
- Completely leak and waterproof.
- Very good Puncture and abrasion resistance
- Ambidextrous design for better and faster wearability
Where to use them:
- Aviation and defense for heavy machinery handling
- Laboratory and commercial cleaning
- Hydraulic repair work
- Corrosive and Radioactive material handling
#13 Hipora fabric
Hipora is a laboratory-created fabric that is breathable yet water-resistant. Made of silicon, it primarily consists of 3 layers. The top layer is completely water-resistant, while the middle layer is porous and allows the innermost layer to breathe and expel the moisture. Hipora is very commonly used as a biking glove material. The layering creates a very well insulated and dry inner glove lining perfect for harsh weather conditions, especially while riding through colder regions.
Advantage:
- Breathable
- Water-resistant
- Very good thermal insulator
- Keeps the palms dry.
Disadvantage:
- Hipora is expensive and not readily available everywhere.
Where to use them:
- Primarily used as liners and inserts for biking gloves, it prevents the hands from getting cold and wet.
#14 Cordura fabric
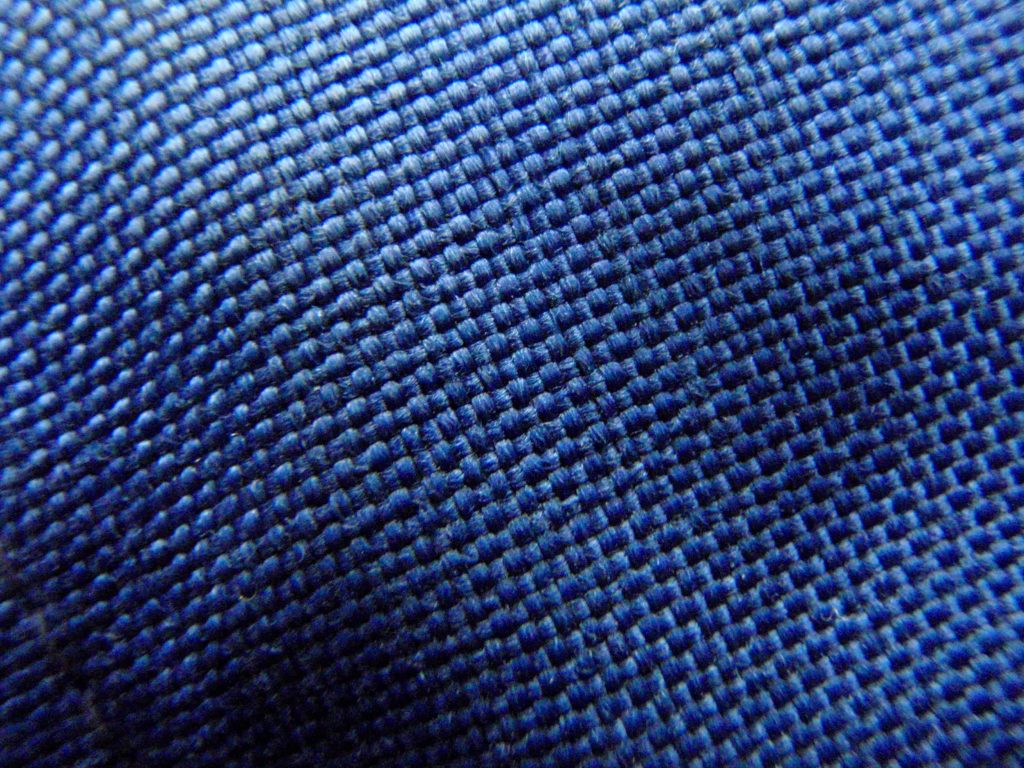

A military-grade fabric, Cordura is a synthetic nylon cotton blend that is highly resistant to wear and tear. Highly resistant to temperature change, Cordura can withstand temperatures as low as 0 degrees without showing distortion. With equally good abrasion resistance, Cordura is used in the making of numerous outdoor applications.
Advantage:
- Lightweight and dextrous
- Long-lasting
- Offers warmth and protection at subzero degrees effortlessly
Disadvantage:
- Heavy and very thick fabric width
- Highly expensive
Where to use them:
- Biking gloves for subzero temperature
- Military uniforms